Welcome to Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Today is
Current Issue
Innovation Article
-
Filamentation extension of femtosecond vortex beams by air density holes
- YANG Lianbin, XU Litong, XI Tingting
-
2023, 40 (4):
433-440.
DOI: 10.7523/j.ucas.2023.024
-
Abstract (
583 )
PDF (0KB) (
0
)
-
We study the influence of air density holes on the filamentation of femtosecond vortex laser beams. The result shows that for the femtosecond vortex laser beams of different initial energies, the filamentation can be greatly elongated by introducing an air density hole which is located near the filamentation onset position. The maximal filamentation length is four times more than that without density hole. The mechanism is that the defocus of the most intense vortex ring induced by air density hole changes the density and distribution of the electrons. As a result, the defocus of trailing pulse edge is weakened, and the trailing edge of femtosecond vortex pulse can refocus, leading to the extension of the filamentation.
Review Article
-
Status of remediation for contaminated sites in developed countries and regions and its enlightenment to China
- ZHAO Dan, YU Fang, LIAO Xiaoyong, WANG Bin, SUN Qian, TAO Huan, WU Weida, ZHOU You
-
2023, 40 (4):
441-452.
DOI: 10.7523/j.ucas.2022.014
-
Abstract (
1037 )
PDF (0KB) (
0
)
-
Status on remediation of contaminated sites in developed countries and regions, such as the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Japan, and Taiwan, were reviewed in this paper, including legislations, pollutants of concern, technologies, source of remediation funds, verification of remediation. Then, the similarities and differences of the five aspects in these five countries and Taiwan with mainland China were compared. The results showed that China had made special legislation for soil pollution prevention and control, the number of contaminated sites is expected to be initially figured out after the detailed soil survey, and the gap with developed countries and regions has been significantly reduced. However, it is still facing the fact that government is mainly responsible for the remediation of historical sites, extensive technology prevails and lone time-consuming verification of remediation. The implementation of the "Soil Pollution Prevention Law" should be taken as an opportunity, combined with the implementation of accountability, effectiveness evaluation, damage compensation and other systems, to properly solve the problem of remediation funds, strictly control historical pollution risks, effectively prevent and control new pollution, build a long-term management mechanism for risk management and restoration of contaminated sites, and maximize environmental, economic and social benefits.
Research Articles
-
Estimation of the structure of K2(
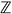 4C2r)
4C2r)
- DENG Wenchao, TANG Guoping
-
2023, 40 (4):
453-455.
DOI: 10.7523/j.ucas.2021.0043
-
Abstract (
768 )
PDF (0KB) (
0
)
-
We already know K2(
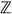 4C2)=(C2)2,K2(
4C2)=(C2)2,K2(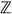 4C4)=(C2)3 from a paper of Zhang Yakun and Tang Guoping(K2 for a kind of special finite group rings). In this paper, we got a set of simplified generators of K2(
4C4)=(C2)3 from a paper of Zhang Yakun and Tang Guoping(K2 for a kind of special finite group rings). In this paper, we got a set of simplified generators of K2(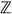 4C2r) by calculating Dennis-Stein symbol in relative K2 group. Then we got the basis for K2(
4C2r) by calculating Dennis-Stein symbol in relative K2 group. Then we got the basis for K2(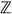 4C2) and K2(
4C2) and K2(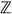 4C4), and we got to know K2(
4C4), and we got to know K2(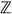 4C8)=(C2)k, 3 ≤ k ≤ 5, K2(
4C8)=(C2)k, 3 ≤ k ≤ 5, K2(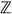 4C2r)=(C2)l,l ≤ 2r-1+1。
4C2r)=(C2)l,l ≤ 2r-1+1。
-
Long-range pair correlations and the Andreev bound state in ferromagnet/ferromagnet/superconductor junctions
- CHEN Chao, JIN Biao
-
2023, 40 (4):
456-467.
DOI: 10.7523/j.ucas.2021.0072
-
Abstract (
742 )
PDF (0KB) (
0
)
-
Based on the Green's function method, we study theoretically the pair correlations and the local density of states (DOS) in a ferromagnet/ferromagnet/s-wave superconductor (F1F2S) heterostructure in the clean limit. The Green's functions which satisfy the Gor'kov equations are calculated numerically without taking the quasiclassical approximation. We find that, when the angle α between the exchange fields in F1 and F2 is finite (α≈0.5π) and further F1 is a half-metal, only the equal-spin triplet correlation can be induced within the F1 layer. In this circumstance, the Andreev reflection is governed by the anomalous equal-spin-band Andreev reflection which can lead to a zero-energy Andreev bound state in the F2 layer. In the presence of the zero-energy Andreev bound state, the induced DOS in the F1 layer exhibits a rather sharp zero-energy peak (ZEP). We derive the condition for the occurrence of the zero-energy Andreev bound state analytically and verify that it can predict the numerical results excellently. In particular, we find that the ZEP structure of DOS can penetrate deep into the F1 layer reflecting the long-range nature of the equal-spin triplet correlation. Experimental detection of the long-range ZEP in our F1F2S system (by using STM, for instance) may provide unambiguous evidence for the presence of the long-range triplet pair correlation induced by the superconducting proximity effect.
-
Physical properties and infrared spectrum characteristics of melamine under external electric fields
- WANG Guocheng, CHEN Yu, ZOU Zhiwei, CAO Runping, LIU Yuzhu
-
2023, 40 (4):
468-473.
DOI: 10.7523/j.ucas.2021.0086
-
Abstract (
811 )
PDF (0KB) (
0
)
-
Melamine (C3H6N6) is an industrial raw material that is extremely harmful to the human body. It is listed as a carcinogen by the World Health Organization. It is particularly important to study its properties under external electric field. In this paper, we have studied the changes of bond length, total energy, dipole moment (induced dipole moment), lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO)-highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) energy gap, Infrared spectroscopy, and dissociation potential energy of C3H6N6 using density functional theory (DFT) at the B3PW91/6-31+ (d, p) basis set level. By calculating the stable electronic structure of the C3H6N6 under external electric fields, the results show that when an electric field is applied in the direction of the N-C bond, the total energy of the C3H6N6 decreases, the dipole moment increases with the increases of the strength of external electric field gradually. On the contrary, the energy gap decreased with the increase of the strength of external field. The electric field has different effects on different bond lengths. As the external electric field gradually increases, the bond length of different N-C bonds changes differently, and the N-H bond length gradually decreases.
-
Spatiotemporal dynamic monitoring and driving factor analysis of ecological carrying capacity in five Central Asian countries
- LI Xu, JIAPAER Guli, YU Tao, YIN Hanmin, TU Haiyang
-
2023, 40 (4):
474-485.
DOI: 10.7523/j.ucas.2021.0085
-
Abstract (
752 )
PDF (0KB) (
0
)
-
The ecological environment in the arid and semi-arid zone of Central Asia is extremely fragile. The aggravation of human activities and unreasonable use of water resources cause the local ecological environment to continuously deteriorate. It is critical to study the ecological carrying capacity of the five Central Asian countries to realize the sustainable development of the region and to ensure the ecological security of the "silk road economic belt". Based on the characteristics of the ecological environment in Central Asia and remote sensing observation methods, this research selected 13 indicators from various aspects of the natural resource supply, ecological environment state and human social activities to establish a long-term monitoring index system of ecological carrying capacity in Central Asia. This research was conducted to reveal the spatiotemporal dynamic characteristics and driving factors of ecological carrying capacity in Central Asia from 2001 to 2019. The results show that the ecological carrying capacity of Central Asia increases from southwest to north and east. In Central Asia, 71.56% of the region's ecological carrying capacity was in a relatively stable condition; 23.93% showed an increasing trend and the farmland ecosystem has been significantly improved; and 4.51% showed a decreasing trend, wetland ecosystem has been significantly decreased. There were four abrupt changes in ecological carrying capacity that occurred in 2003, 2006, 2010 and 2016. The ecological carrying capacity of Central Asia was influenced by both human activities and climate change, drought is the main reason of abrupt changes and fluctuations in ecological carrying capacity, especially on rain-fed farmland and grassland ecosystems in north Central Asia. Human activities are the major driving force affecting the change of ecological carrying capacity in Central Asia, their influences are concentrated in the Aral Sea, Kazakh hills, Turgay depression and farming and oasis areas.
-
Estimation of flood inundation duration using multi-source radar remote sensing in Poyang Lake basin
- ZHANG Ruoxu, LI Xiaotao, JIANG Wei, ZHANG Liping, DENG Qinghai, SONG Xiaoning
-
2023, 40 (4):
486-495.
DOI: 10.7523/j.ucas.2021.0079
-
Abstract (
923 )
PDF (0KB) (
0
)
-
To investigate flood disaster damage at large-scale, it is necessary to propose inundation duration estimation method using multi-source radar remote sensing data. Firstly, Poyang Lake basin flood located in middle of the Yangtze River is taken as study area; and then, multi-temporal radar remote sensing data are collected to extract flood inundation areas using random forest model; moreover, inundation duration is calculated at Poyang Lake basin using the estimation model of inundation duration with multi-temporal inundation areas; finally, the flood disaster assessment is conducted using average inundation duration and relationship of inundation duration and the yield loss degree of rice. The results show that:1) the Kappa coefficients of the flood inundation extracted area are higher than 0.89 and the basin flood inundation lasts 1-44 days; 2) extremely severely flood affected at township scale locate at Nanji, Changzhou, Sanjiao and the most severely flood affected areas mainly locate at Poyang, Lianhu, and Jiaotang. The majority of areas are classified as moderately affected and the assessment results are consistent with the actual disaster damage situation. The proposed inundation duration estimation method has the advantages of large scale monitoring with high frequency, which can provide support for basin flood emergency monitoring and rapid disaster damage assessment.
-
Spatial-temporal evolution simulation and ecological response of urban expansion in Western New City of Chongqing based on CA-Markov model
- WANG Kewen, QIN Jian, MA Haitao
-
2023, 40 (4):
496-505.
DOI: 10.7523/j.ucas.2022.008
-
Abstract (
884 )
PDF (0KB) (
0
)
-
Taking the Western New City of Chongqing as the research area, we compared Markov model and CA-Markov model in simulating the urban expansion so as to verify the advancement of CA-Markov model. Then we used CA-Markov model to predict the urban expansion pattern of the Western New City in 2030, and analyzed the spatial-temporal evolution characteristics and ecological response of urban expansion from 2007 to 2030. The research results show that:1) Compared with Markov model, CA-Markov model has a better area simulation capability and makes up for the former's lack of spatial pattern simulation capability, whose Kappa coefficient is up to 82.97%. 2) The area, rate, and intensity of urban expansion in Western New City of Chongqing from 2007 to 2018 were 1 568.78 hm2, 5.74%, and 1.20%, respectively, while the counterparts predicted from 2018 to 2030 will be 71.62 hm2, 0.15%, and 0.05%, respectively. It shows that the urban development period of Western New City of Chongqing will change from the rapid urbanization stage to the saturation stage of urban expansion. 3) There are significant spatial differences in urban expansion of the study area. The construction land has gradually expanded from the western agglomeration to the "n"-shaped area composed of the west, north, and east in the study area, and it has changed from extensional expansion to internal expansion. 4) The ecological protection and urban expansion in the study area have undergone the evolution process of "joint advancement-confrontation-stability", and the scope of ecological land in some areas will expand in the future. To a certain extent, it has avoided the blind urban expansion, and the development of urban construction and the ecological protection will achieve a better balance. Political factor may play a significantly leading role in the ecological response of Western New City of Chongqing.
-
Efficiency of rural infrastructure construction in increasing farmers' income: a case study of four prefectures in Southern Xinjiang
- SUN Chenxi, DU Hongru
-
2023, 40 (4):
506-513.
DOI: 10.7523/j.ucas.2021.0082
-
Abstract (
787 )
PDF (0KB) (
0
)
-
Rural infrastructure construction has played an important role in targeted poverty alleviation, and the rational and efficient use of rural infrastructure is the key to further realizing rural revitalization. In this paper, super-efficiency DEA method was used to analyze the impact efficiency of rural infrastructure on farmers' income increase in 33 districts and counties of four prefectures in Southern Xinjiang during 2014 to 2019, and the following conclusions were drawn:1) The effect efficiency of rural infrastructure on farmers' income increase in Southern Xinjiang has not been effective and needs to be improved. 2) There are significant regional differences in the impact efficiency of rural infrastructure on farmers' income, and areas with better natural conditions, higher per capita income and larger village population have higher impact efficiency. 3) The impact efficiency growth is not stable, and the fluctuation of technological progress is the main reason for the instability of efficiency growth. In terms of policy, we should focus on promoting the construction of rural infrastructure in low-efficiency areas, strengthening the management, maintenance and supervision of rural infrastructure, and actively guiding farmers to use rural infrastructure, so as to realize the continuous and stable improvement of the efficiency of rural infrastructure on increasing farmers' income and accelerating the rural revitalization.
-
Prediction of landslide displacement based on EEMD-Prophet-LSTM
- WANG Zhenhao, NIE Wen, XU Hanhua, JIAN Wenbin
-
2023, 40 (4):
514-522.
DOI: 10.7523/j.ucas.2022.002
-
Abstract (
946 )
PDF (0KB) (
0
)
-
For the unsteady process of step-type landslide displacement, a method combining ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD), Prophet, and long short time memory network (LSTM) to predict landslide displacement is proposed. The displacement data of Baishuihe landslide was taken as examples. The displacement time series was decomposed into residual(RES) and several intrinsic mode functions(IMF) by EEMD. The superimposition of IMFS which included periodic factors and random factors was considered as a volatility item, and the RES was regarded as a trend term. The trending term was fitted by the Prophet and the the volatility term was predicted by LSTM. The addition of the two prediction results was the predictied value of the landslide displacement. The results show that the coefficient of determination(R2) of the EEMD-Prophet-LSTM model is above 0.98 for Baishuihe landslide displacement prediction, which is better than traditional machine learning methods such as support vector machine and artificial neural network. Moreover, the prediction accuracy R2 of this method for each monitoring point of the Bazimen landslide is also above 0.96, which proves the applicability of this method.
-
Screening method of remote sensing image region covering dataset
- YAN Xuejing, LIU Wei, LIU Shibin, DUAN Jianbo, XIA Wei
-
2023, 40 (4):
523-530.
DOI: 10.7523/j.ucas.2022.006
-
Abstract (
1195 )
PDF (0KB) (
0
)
-
With the development of remote sensing satellite technology, the temporal and spatial resolution of remote sensing data has been continuously improved, showing the trend of big data and massive quantification, which has brought challenges to the screening of remote sensing data. Traditional remote sensing data retrieval often has the problem of large amount of query results and high overlap. It requires manual data selection, which is inefficient and low in accuracy. Therefore, how to quickly and accurately find the required data from a large number of remote sensing images is a problem that needs to be solved urgently. In this paper, a remote sensing data screening algorithm based on area coverage is used to divide the target area into non-overlapping fragments using the effective range of images. A normalized mathematical calculation model is established based on the number of fragments contained in the image, imaging time, and cloud cover. The model obtains a comprehensive cost. An optimal image combination is selected according to the cost, which completely covers the target area. This paper confirms the effectiveness of the method through Landsat8 data, and improves the screening efficiency through parallel computing.
-
School place identification based on improved YOLOv3
- GAO Jinfeng, CHEN Yu, WEI Yongming, LI Jiannan, JIANG Ruonan
-
2023, 40 (4):
531-539.
DOI: 10.7523/j.ucas.2021.0081
-
Abstract (
964 )
PDF (0KB) (
0
)
-
The specific place identification based on remote sensing images is of great significance in smart city planning, land use analysis, and safe city construction. However, it is difficult to identify these places with simple rules by using traditional classification or target recognition methods due to the complex environmental background. Convolutional neural networks have strong spatial information mining capabilities. In this article, we improved the well-known YOLOv3 model to a new model called YOLO-S-CIoU for school place identification. The main improvements include:1) Using the SRXnet module to replace the Darknet53 module in YOLOv3 to improve the feature learning ability; 2) Using complete-IoU loss (CIoU loss) to optimize the regression of the bounding box; 3) Training and verification based on self-made school place sample dataset (SS dataset). The results showed that the average accuracy (AP) of YOLO-S-CIoU reached 96.46%; the parameter amount was 226 MB. Compared with YOLOv3, YOLO-S-CIoU has achieved a 9 MB reduction in parameter volume and a 2.3% increase in AP. In addition, in the regional remote sensing images of Tumshuk and Yantai, the recall rates of school places were increased by 37.5% and 42.2% than YOLOv3, respectively. These works show that the improved model has stronger robustness and higher identification ability in remote sensing image identification in different areas.
-
Voxel-based meshing collision detection accelerating algorithm for DDA2D
- CHENG Xiaolong, CHENG Zhangyan, XIAO Jun, ZHANG Long, WANG Ying
-
2023, 40 (4):
540-546.
DOI: 10.7523/j.ucas.2021.0071
-
Abstract (
666 )
PDF (0KB) (
0
)
-
Contact detection takes the most time in the calculation process of discontinuous deformation analysis method. Contact detection consists of two steps:contact coarse detection and contact precise detection; contact coarse detection searches all possible block pairs in the calculation space; the contact precise detection determines the specific contact position for the block pairs from the contact coarse detection results for subsequent mechanical treatment. In this paper, an efficient contact coarse detection algorithm based on voxel meshing is proposed. The algorithm divides the complex blocks that meet the specific conditions into sub grids, which effectively reduces the number of generated pre-detected blocks. The algorithm has been integrated into the discontinuous deformation analysis program and tested by classical examples. The results show that the proposed algorithm has obvious advantages over the existing algorithms.
-
An economical scanning digital measurement system
- WANG Mengxing, FENG Yifei, YANG Dongyu, SHEN Liyong
-
2023, 40 (4):
547-554.
DOI: 10.7523/j.ucas.2023.002
-
Abstract (
601 )
PDF (0KB) (
0
)
-
The non-contact measurement and reconstruction are widely used in industrial applications, however, the price of low-end equipment in the market is expensive. In this paper, an economical 3D non-contact scanner is built based on laser triangulation method, and the methods of object scanning, geometric reconstruction and measurement are implemented by combining data processing and geometric reconstruction. Compared with the comparative commercial scanners, the system in this paper has certain advantages in the range of view, data quality, reconstruction results and geodesic distance estimation. At the same time, our algorithm can effectively deal with the reflection of metal objects and has good performance in extreme cases. The experimental results show that the proposed non-contact scanning platform process is suitable for the implementation and evaluation of economical scanning digital measurement systems, and can be used to build cost-effective digital measurement systems.
-
Kinematics application calibration method of collaborative robot
- LI Haiwang, SUI Chunping, WANG Yukun, SHAN Tianya, HUO Shaoda
-
2023, 40 (4):
555-565.
DOI: 10.7523/j.ucas.2021.0083
-
Abstract (
998 )
PDF (0KB) (
0
)
-
The geometric parameter error of robot leads to its poor absolute positioning accuracy, which restricts its application in off-line programming. The joint stiffness of the collaborative robot is small, so its flexible deformation is largely affected by its self-weight and end load, which further reduce its positioning accuracy. Aiming at this problem, the kinematics calibration method of adjacent three-axis parallel(2-4 axis) cooperative robot is studied, and the corresponding calibration software is developed to apply the method to engineering practice. Firstly, a nonlinear geometric parameter identification model is proposed, and the redundancy of the model parameters is analyzed by using the inverse function principle of the model's nonlinear equations. Further, a joint stiffness identification model is established. Considering the mutual interference between geometric parameter identification and joint stiffness identification, a comprehensive identification method based on iterative thought is proposed. The calibration experiment of UR5 robot is carried out using this method. The experimental results show that the absolute positioning accuracy of the robot under no-load and load after calibration is improved by 75.5% and 85.1%, respectively, compared with that before calibration, which verifies the effectiveness of the calibration method in this paper.
-
A fuel price recommendation model based on the sliced recurrent neural network under sales constraints
- LIAN Huiqiang, LIU Bing, LI Pengyuan, YU Hua
-
2023, 40 (4):
566-576.
DOI: 10.7523/j.ucas.2021.0056
-
Abstract (
924 )
PDF (0KB) (
0
)
-
Determining the retail fuel price for the petrol stations is essential for the development of smart petrol stations. Since the changes in the fuel price follow a complex nonlinear model, the nonlinear time series mode represented by long short-term memory (LSTM) have improved the accuracy of traditional time series forecasting methods, though, its running efficiency is still difficult to meet the dynamic demand of oil price forecasting. To address this issue, in this paper we propose a fuel price recommendation model based on the sliced recurrent neural network (SRNN) with an LSTM model as the recurrent unit under the sales constraints. We further train this model and evaluate its learning parameters, such as learning rate, based on 4 years of historical data. In our evaluations, we utilize real data from petrol stations. Results show that our proposed model achieves the same level of accuracy as that of the LSTM neural network; however, it is 72 times faster than that of the LSTM neural network. Besides, the fuel price recommendation model based on the SRNN is efficiently applied to real petrol stations hence confirmed its practical value.
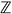 4C2r)
4C2r)
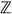 4C2)=(C2)2,K2(
4C2)=(C2)2,K2(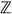 4C4)=(C2)3 from a paper of Zhang Yakun and Tang Guoping(K2 for a kind of special finite group rings). In this paper, we got a set of simplified generators of K2(
4C4)=(C2)3 from a paper of Zhang Yakun and Tang Guoping(K2 for a kind of special finite group rings). In this paper, we got a set of simplified generators of K2(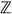 4C2r) by calculating Dennis-Stein symbol in relative K2 group. Then we got the basis for K2(
4C2r) by calculating Dennis-Stein symbol in relative K2 group. Then we got the basis for K2(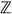 4C2) and K2(
4C2) and K2(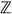 4C4), and we got to know K2(
4C4), and we got to know K2(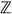 4C8)=(C2)k, 3 ≤ k ≤ 5, K2(
4C8)=(C2)k, 3 ≤ k ≤ 5, K2(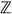 4C2r)=(C2)l,l ≤ 2r-1+1。
4C2r)=(C2)l,l ≤ 2r-1+1。