中国科学院大学学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 93-103.DOI: 10.7523/j.ucas.2024.019
孙瑞奇1,2, 张文娟1( ), 李震1, 马雪松3, 梅君林1,2
), 李震1, 马雪松3, 梅君林1,2
收稿日期:2024-01-19
修回日期:2024-04-03
发布日期:2024-05-09
通讯作者:
张文娟
基金资助:
Ruiqi SUN1,2, Wenjuan ZHANG1( ), Zhen LI1, Xuesong MA3, Junlin MEI1,2
), Zhen LI1, Xuesong MA3, Junlin MEI1,2
Received:2024-01-19
Revised:2024-04-03
Published:2024-05-09
Contact:
Wenjuan ZHANG
摘要:
以高空间分辨率(高分)遥感图像为对象,采用3种典型超分模型,开展9组不同分块尺寸实验,研究其对整图超分精度和效率的影响。综合分析结果如下:1)分块超分导致拼接缝,当分块较小时,拼接缝呈现斑块效应,不一致性更为显著;2)随着分块尺寸增大,模型的超分精度和计算效率均有所提高,当分块比大于1时,耗时与精度趋于稳定;3)整图输入的计算可行性、精度和模型关系密切。ESPCN模型在整图输入时精度最优,RDBPN模型由于图像非方阵而导致精度下降,HSENET模型对算力要求较高,无法进行整图计算。综上,该研究为遥感超分工程化应用的分块尺寸选取提供了实验依据。
中图分类号:
孙瑞奇, 张文娟, 李震, 马雪松, 梅君林. 分块尺寸对大场景遥感图像空间超分应用的影响分析[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2026, 43(1): 93-103.
Ruiqi SUN, Wenjuan ZHANG, Zhen LI, Xuesong MA, Junlin MEI. Effect of patch size on super-resolution of large scene remote sensing images[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2026, 43(1): 93-103.
| 分块比 | 切块尺寸 | 切块数量 |
|---|---|---|
| 1/16 | 12 | 983 040 |
| 1/8 | 24 | 245 760 |
| 1/4 | 48 | 61 440 |
| 1/2 | 96 | 15 360 |
| 1 | 192 | 3 840 |
| 2 | 384 | 960 |
| 4 | 768 | 240 |
| 8 | 1 536 | 60 |
表 1 实验所用图像的分块尺寸与数量
Table 1 Patch size and number of patches of the image used in the experiment
| 分块比 | 切块尺寸 | 切块数量 |
|---|---|---|
| 1/16 | 12 | 983 040 |
| 1/8 | 24 | 245 760 |
| 1/4 | 48 | 61 440 |
| 1/2 | 96 | 15 360 |
| 1 | 192 | 3 840 |
| 2 | 384 | 960 |
| 4 | 768 | 240 |
| 8 | 1 536 | 60 |
| 模型名称 | 参数量/M | 浮点运算数/G |
|---|---|---|
| ESPCN | 0.45 | 1.44 |
| RDBPN | 15.20 | 4.91 |
| HSENET | 5.43 | 10.79 |
表 2 实验所选模型主要参数情况
Table 2 Main parameters of the selected model in the experiment
| 模型名称 | 参数量/M | 浮点运算数/G |
|---|---|---|
| ESPCN | 0.45 | 1.44 |
| RDBPN | 15.20 | 4.91 |
| HSENET | 5.43 | 10.79 |
| 分块比 | ΔPSNR(dB)/ΔSSIM | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ESPCN | RDBPN | HSENET | |
| 1/16 | — | — | — |
| 1/8 | 0.522 8/0.098 0 | 0.279 0/0.037 4 | 0.231 8/0.035 8 |
| 1/4 | 0.073 4/0.018 4 | 0.113 8/0.013 9 | 0.153 6/0.015 6 |
| 1/2 | 0.027 1/0.007 0 | 0.054 9/0.006 6 | 0.084 1/0.007 6 |
| 1 | 0.010 4/0.002 9 | 0.025 4/0.003 2 | 0.044 8/0.003 7 |
| 2 | 0.004 7/0.001 3 | 0.012 6/0.001 6 | 0.024 9/0.001 7 |
| 4 | 0.001 8/0.000 6 | 0.005 9/0.000 8 | 0.015 9/0.000 7 |
| 8 | 0.001 1/0.000 3 | 0.003 0/0.000 4 | 内存不足(out of memory) |
| 16 | 0.000 6/0.000 1 | 0.001 9/0.000 2 | 内存不足(out of memory) |
表 3 随着分块比的提升各模型PSNR和SSIM的变化量
Table 3 PSNR and SSIM changes of each model as the ratio of test block size to training block size increases
| 分块比 | ΔPSNR(dB)/ΔSSIM | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ESPCN | RDBPN | HSENET | |
| 1/16 | — | — | — |
| 1/8 | 0.522 8/0.098 0 | 0.279 0/0.037 4 | 0.231 8/0.035 8 |
| 1/4 | 0.073 4/0.018 4 | 0.113 8/0.013 9 | 0.153 6/0.015 6 |
| 1/2 | 0.027 1/0.007 0 | 0.054 9/0.006 6 | 0.084 1/0.007 6 |
| 1 | 0.010 4/0.002 9 | 0.025 4/0.003 2 | 0.044 8/0.003 7 |
| 2 | 0.004 7/0.001 3 | 0.012 6/0.001 6 | 0.024 9/0.001 7 |
| 4 | 0.001 8/0.000 6 | 0.005 9/0.000 8 | 0.015 9/0.000 7 |
| 8 | 0.001 1/0.000 3 | 0.003 0/0.000 4 | 内存不足(out of memory) |
| 16 | 0.000 6/0.000 1 | 0.001 9/0.000 2 | 内存不足(out of memory) |
| 分块比 | PSNR(dB)/SSIM | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ESPCN | RDBPN | HSENET | |
| 21.020 8/0.452 6 | 21.810 5/0.563 1 | 21.830 0/0.566 1 | |
| 21.543 6/0.550 6 | 22.089 4/0.600 5 | 22.061 8/0.601 7 | |
| 21.617 0/0.569 0 | 22.203 2/0.614 4 | 22.215 4/0.6173 | |
| 21.644 1/0.576 1 | 22.258 1/0.621 0 | 22.299 5/0.624 9 | |
| 1 | 21.654 5/0.579 0 | 22.283 5/0.624 2 | 22.344 2/0.628 6 |
| 2 | 21.659 1/0.580 3 | 22.296 2/0.625 8 | 22.369 1/0.630 2 |
| 4 | 21.660 9/0.580 9 | 22.302 1/0.626 6 | 22.385 1/0.631 0 |
| 8 | 21.662 0/0.581 2 | 23.305 1/0.627 0 | *内存不足(out of memory) |
| 16 | 21.662 7/0.581 4 | 23.307 1/0.627 2 | *内存不足(out of memory) |
| 整块输入 | 21.663 0/0.581 5 | *21.756 5/0.520 3 | *内存不足(out of memory) |
表 4 分块尺寸与各模型PSNR和SSIM
Table 4 Patch size versus PSNR and SSIM of each model
| 分块比 | PSNR(dB)/SSIM | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ESPCN | RDBPN | HSENET | |
| 21.020 8/0.452 6 | 21.810 5/0.563 1 | 21.830 0/0.566 1 | |
| 21.543 6/0.550 6 | 22.089 4/0.600 5 | 22.061 8/0.601 7 | |
| 21.617 0/0.569 0 | 22.203 2/0.614 4 | 22.215 4/0.6173 | |
| 21.644 1/0.576 1 | 22.258 1/0.621 0 | 22.299 5/0.624 9 | |
| 1 | 21.654 5/0.579 0 | 22.283 5/0.624 2 | 22.344 2/0.628 6 |
| 2 | 21.659 1/0.580 3 | 22.296 2/0.625 8 | 22.369 1/0.630 2 |
| 4 | 21.660 9/0.580 9 | 22.302 1/0.626 6 | 22.385 1/0.631 0 |
| 8 | 21.662 0/0.581 2 | 23.305 1/0.627 0 | *内存不足(out of memory) |
| 16 | 21.662 7/0.581 4 | 23.307 1/0.627 2 | *内存不足(out of memory) |
| 整块输入 | 21.663 0/0.581 5 | *21.756 5/0.520 3 | *内存不足(out of memory) |
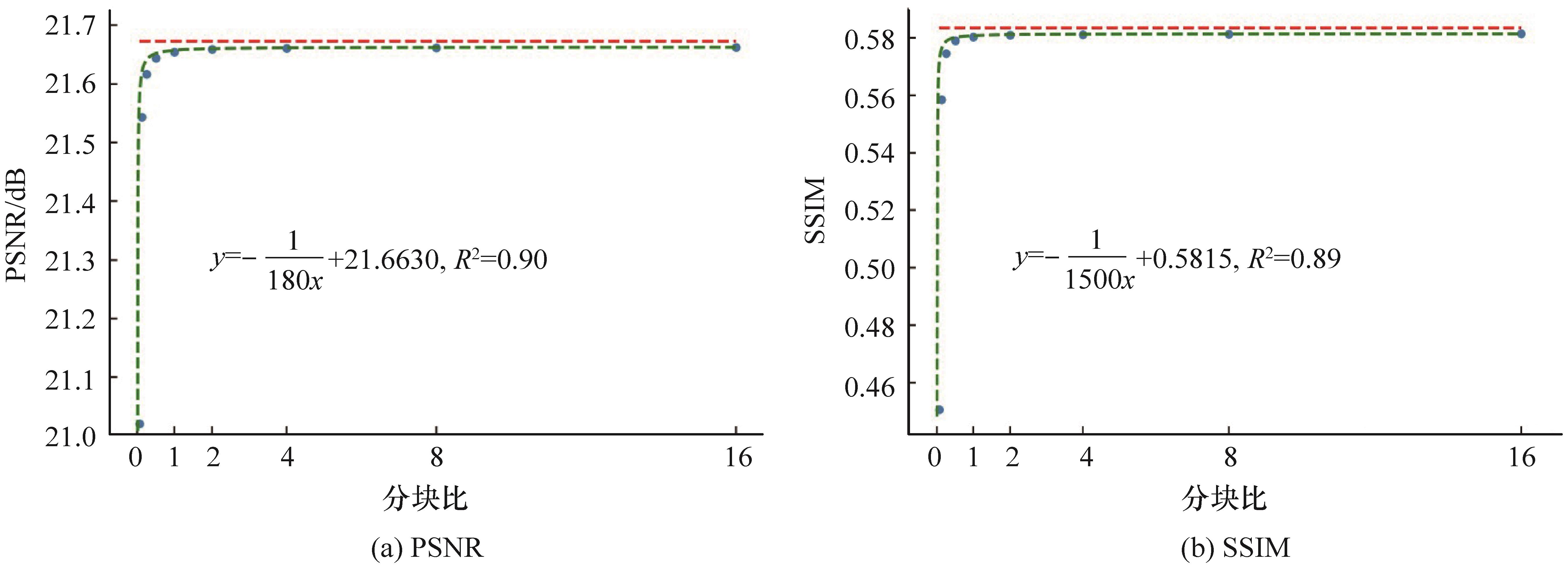
图7 ESPCN输入整块时的重建指标以及分块比和指标的参量(PSNR、SSIM)拟合情况
Fig.7 PSNR and SSIM when ESPCN inputs the whole RSI, and the parameterfitting of the ratio of the test block to the training block
| [1] | 张兵.当代遥感科技发展的现状与未来展望[J].中国科学院院刊,2017,32(7):774-784.DOI:10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.2017.07.012 . |
| [2] | 黄昕, 张良培, 李平湘. 高空间分辨率遥感图像分类的SSMC方法[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2006, 11(4): 529-534, 插4. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8961.2006.04.014 . |
| [3] | Martins V S, Kaleita A L, Gelder B K, et al. Exploring multiscale object-based convolutional neural network (multi-OCNN) for remote sensing image classification at high spatial resolution[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 168: 56-73. DOI: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.08.004 . |
| [4] | 张鑫龙, 陈秀万, 李飞, 等. 高分辨率遥感影像的深度学习变化检测方法[J]. 测绘学报, 2017, 46(8): 999-1008. DOI: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170036 . |
| [5] | Fytsilis A L, Prokos A, Koutroumbas K D, et al. A methodology for near real-time change detection between Unmanned Aerial Vehicle and wide area satellite images[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2016, 119: 165-186. DOI: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2016.06.001 . |
| [6] | 林祥国, 张继贤. 面向对象的形态学建筑物指数及其高分辨率遥感影像建筑物提取应用[J]. 测绘学报, 2017, 46(6): 724-733. DOI: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170068 . |
| [7] | Sun X, Wang P J, Yan Z Y, et al. FAIR1M: a benchmark dataset for fine-grained object recognition in high-resolution remote sensing imagery[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2022, 184: 116-130. DOI: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2021.12.004 . |
| [8] | 郑凯旋, 林兴稳, 闻建光, 等. 集合卡尔曼滤波方法的高时空分辨率山区 地表反照率反演[J]. 遥感学报, 2022, 26(12): 2568-2581. DOI: 10.11834/jrs.20210322 . |
| [9] | Huang L, Han X Y, Wang X L, et al. Coupling with high-resolution remote sensing data to evaluate urban non-point source pollution in Tongzhou, China[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 831: 154632. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154632 . |
| [10] | 左超, 陈钱. 计算光学成像: 何来, 何处, 何去, 何从?[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2022, 51(2): 150-330. DOI: 10.3788/IRLA20220110 . |
| [11] | 左超, 陈钱. 分辨率, 超分辨率与空间带宽积拓展:从计算光学成像角度的一些思考[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2022(6): 1105-1166. DOI: 10.37188/CO.2022-0105 . |
| [12] | 郑珂. 基于深度学习的高光谱图像超分辨率重建与分类方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学 (北京), 2020. DOI: 10.27624/d.cnki.gzkbu.2020.000027 . |
| [13] | 李佳星, 赵勇先, 王京华. 基于深度学习的单幅图像超分辨率重建算法综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(10): 2341-2363. DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c190859 . |
| [14] | Keys R. Cubic convolution interpolation for digital image processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1981, 29(6): 1153-1160. DOI: 10.1109/TASSP.1981.1163711 . |
| [15] | Wang Q M, Shi W Z, Atkinson P M. Sub-pixel mapping of remote sensing images based on radial basis function interpolation[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2014, 92: 1-15. DOI: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2014.02.012 . |
| [16] | Ma J L, Chan J C W, Canters F. Robust locally weighted regression for super-resolution enhancement of multi-angle remote sensing imagery[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(4): 1357-1371. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2312887 . |
| [17] | Wang P, Yao H Y, Li C, et al. Multiresolution analysis based on dual-scale regression for pansharpening[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5406319. DOI: 10.1109/tgrs.2021.3131477 . |
| [18] | Pan Z X, Yu J, Huang H J, et al. Super-resolution based on compressive sensing and structural self-similarity for remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(9): 4864-4876. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2230270 . |
| [19] | Hou B, Zhou K, Jiao L C. Adaptive super-resolution for remote sensing images based on sparse representation with global joint dictionary model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(4): 2312-2327. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2778191 . |
| [20] | Jiang K, Wang Z Y, Yi P, et al. Edge-enhanced GAN for remote sensing image superresolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(8): 5799-5812. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2902431 . |
| [21] | Xu M Z, Ma J, Zhu Y Y. Dual-Diffusion: dual conditional denoising diffusion probabilistic models for blind super-resolution reconstruction in RSIs[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 6008505. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3304418 . |
| [22] | Dong C, Loy C C, He K M, et al. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(2): 295-307. DOI: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2439281 . |
| [23] | Shi W Z, Caballero J, Huszár F, et al. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, NV, USA. IEEE, 2016: 1874-1883. DOI: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.207 . |
| [24] | Pan Z X, Ma W, Guo J Y, et al. Super-resolution of single remote sensing image based on residual dense backprojection networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(10): 7918-7933. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2917427 . |
| [25] | Lei S, Shi Z W. Hybrid-scale self-similarity exploitation for remote sensing image super-resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5401410. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3069889 . |
| [26] | Ji S P, Wei S Q, Lu M. Fully convolutional networks for multisource building extraction from an open aerial and satellite imagery data set[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(1): 574-586. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2858817 . |
| [27] | Odena A, Dumoulin V, Olah C. Deconvolution and checkerboard artifacts[J]. Distill, 2016, 1(10): e3. DOI: 10.23915/distill.00003 . |
| [1] | 赵佳祎, 马勇, 陈甫, 姚武韬, 尚二萍, 仉淑艳, 龙安. 面向真实场景的高分辨率遥感影像超分辨率重建[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2026, 43(1): 80-92. |
| [2] | 熊世梅, 许文强, 包安明, 王正宇, 陶泽涪. 基于无人机LiDAR数据的荒漠梭梭林单木分割[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2025, 42(5): 700-710. |
| [3] | 周庆泽, 郭擎. 多重残差网络的多光谱遥感图像锐化方法[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2025, 42(4): 565-575. |
| [4] | 曾建顺, 吕炎杰, 覃驭楚. 基于多尺度语义先验的街景图像修复算法[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2025, 42(4): 496-507. |
| [5] | 钟金彦, 陈俊, 李宇, 吴业炜, 葛小青. 基于MFF-SFE的遥感图文跨模态检索方法[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2025, 42(2): 236-247. |
| [6] | 周文雪, 张华春. 一种面向SAR图像快速舰船检测的轻量化网络[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2024, 41(6): 776-785. |
| [7] | 喻永生, 罗铁坚. 基于GAN反演的无缝图像补全技术[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2024, 41(5): 705-714. |
| [8] | 陈经纬, 李宇, 陈俊, 张洪群. 基于MFF-Deeplabv3+网络的高分辨率遥感影像建筑物提取方法[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2024, 41(5): 654-664. |
| [9] | 黄玉林, 梁磊, 李卫军, 习晓环. 基于多尺度特征和注意力机制的深度学习点云压缩[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2024, 41(5): 687-694. |
| [10] | 林昱彤, 王红, 柴团耀. 基于卷积神经网络多尺度特征的大豆基因组表型预测[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2024, 41(4): 468-476. |
| [11] | 肖俊, 石光田. 三维点云去噪技术[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2023, 40(5): 577-595. |
| [12] | 姚沐风, 昝露洋, 李柏鹏, 李庆亭, 陈正超. 基于CAR-Siamese网络的高分辨率遥感图像建筑物变化检测[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2023, 40(3): 380-387. |
| [13] | 盛晓光, 王颖, 张迎伟, 项若曦, 付红萍. WILS:面向学业预警的非均衡增量式学习方法[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2023, 40(3): 422-432. |
| [14] | 陈若男, 彭玲, 刘玉菲, 卫志超, 吕蓓茹, 陈德跃. 引入空间距离信息的城郊山区道路提取与应用[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2022, 39(5): 658-667. |
| [15] | 古煜民, 阎福礼. 基于不同骨架UNet++网络的建筑物提取[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2022, 39(4): 512-523. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
